As an athlete, ensuring that you get enough protein is crucial for muscle recovery, strength, and overall performance. Traditionally, animal products have been the go-to source for protein. However, more athletes are turning to plant-based proteins for their health benefits, ethical reasons, and environmental concerns. This guide will help you understand the best sources of plant-based proteins and how to incorporate them into your diet effectively.
Why Choose Plant-Based Proteins?
- Health Benefits: Plant-based proteins are typically lower in saturated fat and cholesterol, reducing the risk of heart disease. They are also rich in fiber, vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, which contribute to overall health.
- Environmental Impact: Producing plant-based proteins generally requires less water and land and produces fewer greenhouse gases compared to animal protein production.
- Ethical Reasons: Many athletes choose plant-based diets to avoid contributing to animal suffering and exploitation.
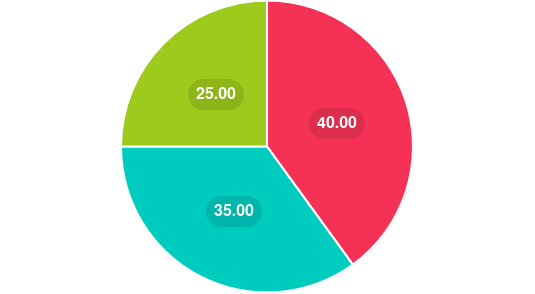
Here’s a pie chart illustrating the reasons why athletes might choose plant-based proteins:
- Health Benefits: 40%
- Environmental Impact: 35%
- Ethical Reasons: 25%
This chart highlights the primary motivations for incorporating plant-based proteins into an athlete’s diet. The largest segment, health benefits, underscores the nutritional advantages, while the environmental impact and ethical reasons also play significant roles in this choice.
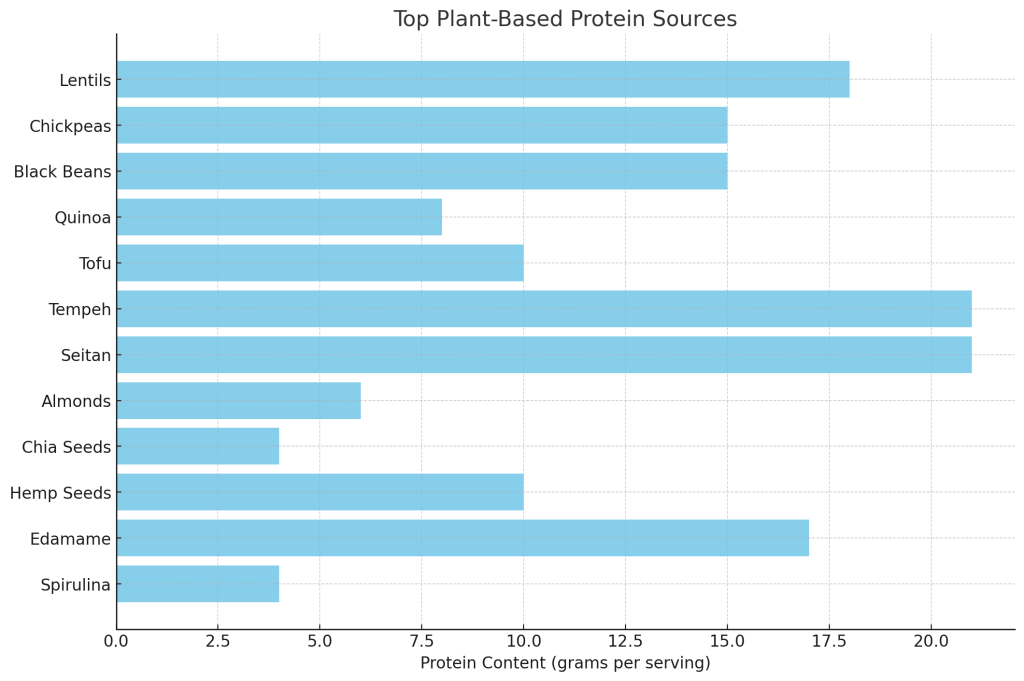
Top Plant-Based Protein Sources
- Legumes: Beans, lentils, and chickpeas are excellent sources of protein. They are versatile and can be used in soups, stews, salads, and as meat substitutes in various dishes.
- Protein Content: Lentils (18g per cup cooked), chickpeas (15g per cup cooked), black beans (15g per cup cooked).
- Quinoa: A complete protein containing all nine essential amino acids, quinoa is a great addition to any meal.
- Protein Content: 8g per cup cooked.
- Tofu and Tempeh: Made from soybeans, tofu and tempeh are highly versatile and can be used in a variety of dishes from stir-fries to sandwiches.
- Protein Content: Tofu (10g per ½ cup), Tempeh (21g per ½ cup).
- Seitan: Made from wheat gluten, seitan is a high-protein meat substitute with a texture similar to chicken.
- Protein Content: 21g per ⅓ cup.
- Nuts and Seeds: Almonds, peanuts, chia seeds, and hemp seeds are not only high in protein but also provide healthy fats.
- Protein Content: Almonds (6g per ounce), chia seeds (4g per ounce), hemp seeds (10g per ounce).
- Edamame: Young soybeans are a great snack or addition to salads and stir-fries.
- Protein Content: 17g per cup cooked.
- Spirulina: This blue-green algae is a complete protein source and can be added to smoothies and shakes.
- Protein Content: 4g per tablespoon.
How to Incorporate Plant-Based Proteins into Your Diet
- Start Your Day Right: Incorporate protein-rich foods like chia seeds, hemp seeds, or peanut butter into your breakfast. Smoothies with protein powder, oats with almond butter, or tofu scramble are excellent choices.
- Protein-Packed Snacks: Keep snacks like roasted chickpeas, nuts, and protein bars handy. These will help maintain your energy levels between meals.
- Balanced Meals: Ensure each meal contains a source of protein. Add beans to salads, quinoa to soups, or tempeh to stir-fries.
- Experiment with Recipes: Try new recipes that focus on plant-based proteins. There are plenty of creative ways to make delicious and protein-rich meals without relying on animal products.
- Use Protein Powders: Plant-based protein powders made from peas, rice, hemp, or soy can be added to shakes, smoothies, and even baked goods to ensure you meet your protein needs.
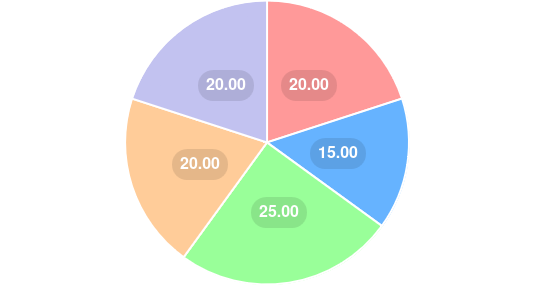
Here’s the pie chart with titles for each section, illustrating different ways to incorporate plant-based proteins into your diet:
- Start Your Day Right: 20%
- Protein-Packed Snacks: 15%
- Balanced Meals: 25%
- Experiment with Recipes: 20%
- Use Protein Powders: 20%
This chart highlights the importance of various strategies to ensure you’re getting enough plant-based protein throughout the day.
Tips for Athletes
- Monitor Your Intake: Athletes generally need more protein than the average person. Aim for 1.2 to 2.0 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight per day, depending on your training intensity and goals.
- Diverse Sources: To ensure you’re getting all essential amino acids, consume a variety of protein sources throughout the day.
- Plan Ahead: Meal prepping can help ensure you have protein-rich meals and snacks readily available, preventing the temptation to reach for less nutritious options.
- Stay Hydrated: Consuming high-protein foods can increase your body’s need for water. Make sure you drink plenty of fluids throughout the day.
- Consult a Nutritionist: If you have specific dietary needs or training goals, consulting with a nutritionist who understands plant-based diets can help you create a tailored eating plan.
Sample Meal Plan for Plant-Based Athletes
| Meal | Menu |
| Breakfast | Quinoa Porridge with almond milk, sliced almonds, chia seeds, and fresh berries. Green Smoothie with spinach, banana, frozen berries, pea protein powder, and flax seeds. |
| Morning Snack | Hummus with sliced carrots, cucumbers, and bell peppers. Lightly salted edamame. |
| Lunch | Chickpea Salad with mixed greens, roasted chickpeas, cherry tomatoes, cucumbers, red onions, and tahini dressing. Lentil Soup. |
| Afternoon Snack | Plant-based protein bar. Trail mix with nuts, seeds, and dried fruits. |
| Dinner | Tofu Stir-Fry with broccoli, bell peppers, snap peas, carrots over brown rice. Black Bean Tacos with corn tortillas, avocado, salsa, and shredded lettuce. |
| Evening Snack | Plant-based yogurt with granola and honey. Spirulina Smoothie with banana and almond milk. |
Here’s a sample meal plan to give you an idea of how to incorporate plant-based proteins throughout your day:
Breakfast:
- Quinoa Porridge: Cooked quinoa with almond milk, topped with sliced almonds, chia seeds, and fresh berries.
- Green Smoothie: Spinach, banana, frozen berries, a scoop of pea protein powder, and flax seeds blended with water or plant-based milk.
Morning Snack:
- Hummus and Veggies: A serving of hummus with sliced carrots, cucumbers, and bell peppers.
- Edamame: Lightly salted edamame beans.
Lunch:
- Chickpea Salad: Mixed greens with roasted chickpeas, cherry tomatoes, cucumbers, red onions, and a tahini dressing.
- Lentil Soup: A hearty bowl of lentil soup with vegetables.
Afternoon Snack:
- Protein Bar: A plant-based protein bar.
- Trail Mix: A mix of nuts, seeds, and dried fruits.
Dinner:
- Tofu Stir-Fry: Stir-fried tofu with broccoli, bell peppers, snap peas, and carrots over brown rice.
- Black Bean Tacos: Corn tortillas filled with black beans, avocado, salsa, and shredded lettuce.
Evening Snack:
- Greek Yogurt Alternative: A plant-based yogurt with granola and a drizzle of honey.
- Spirulina Smoothie: A small smoothie with spirulina, banana, and almond milk.
Supplementation
While whole foods should be your primary source of nutrients, some athletes might find it beneficial to supplement their diet, especially if they have specific dietary restrictions or intense training regimens. Here are a few supplements to consider:
- Vitamin B12: Since B12 is primarily found in animal products, consider taking a B12 supplement to prevent deficiency.
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids: Algae-based supplements can provide essential omega-3s, which are crucial for heart and brain health.
- Iron: Plant-based sources of iron are less readily absorbed by the body, so you might need a supplement, especially if you’re prone to anemia.
- Protein Powders: To meet high protein needs, plant-based protein powders (like pea, hemp, or soy protein) can be a convenient option.
Transitioning to a plant-based diet as an athlete can be incredibly rewarding. Not only can you meet your protein needs, but you can also enjoy a variety of health benefits, contribute to a more sustainable environment, and make ethical food choices. With careful planning and a diverse range of protein sources, you can thrive and excel in your athletic endeavors while enjoying a plant-based lifestyle. Remember, consistency and variety are key to ensuring you get all the necessary nutrients for optimal performance and recovery.
Switching to a plant-based diet as an athlete doesn’t mean sacrificing protein or performance. By understanding and incorporating a variety of plant-based protein sources, you can meet your nutritional needs, support muscle recovery, and maintain peak performance while enjoying the many health and environmental benefits of a plant-based lifestyle.



